A poison is anything that in the "right" amount might be harmful if you taste, breathe, or touch it.
Did you know?
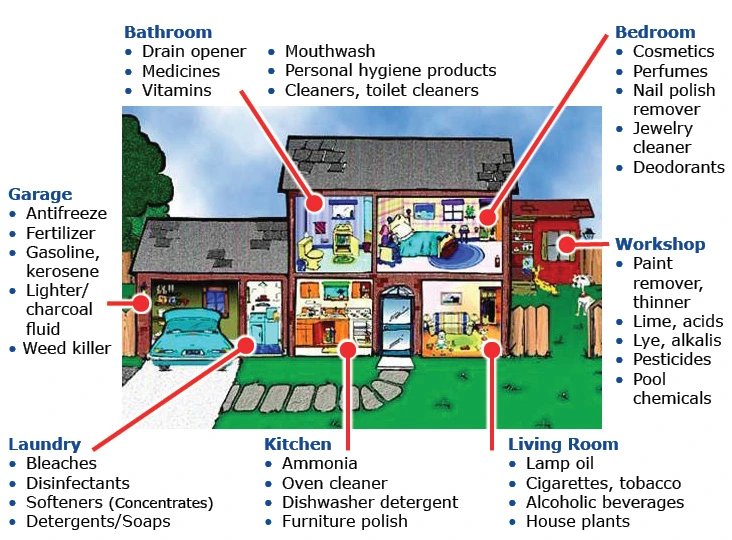
- Products found in the home are responsible for most accidental poisonings among children.
- Most homes contain more than 100 products that can be harmful if you taste, breathe or touch them.
- Most poisonings from household products, to children and adults, occur when the product is in use, not when it is stored.
- Children under 5 are the most likely to eat, drink, inhale or splash themselves with toxic products.
- Over-the-counter medications are involved in more poison emergencies than prescription medications.
Factors that contribute to a poisoning:
- Poisonous products are not put away immediately after use.
- Poisonous products are stored in food or drink containers.
- Empty product containers are discarded improperly.
- At least one child in the family is under the age of 5.
- Stressful situations or changes in the household's routine (illness, holidays).
First aid for poisoning
Is the person unconscious or not breathing? Call 911.
If the person has not collapsed, call the poison center right away: 1-800-222-1222
For the following situations:
- Swallowed poison - Do not make the person vomit, do not give anything by mouth.
- Inhaled poison - Get to fresh air right away.
- Poison in the eye - Rinse eye(s) with running water for 15 minutes. Don't force the eyelids open.
- Poison on the skin - Remove any clothing that the poison touched, run tap water over the skin for 15 minutes.
Bite or sting by a venomous creature:
Call 1-800-222-1222
Prevention tips
- Anticipate your child's developmental stages.
- Don't leave a child and a poison alone together even "for a second."
- Never tell children medicine "tastes like candy."
- Give medicine only to the person the doctor has prescribed it for.
- Don't take or give medicines in the dark or without reading the label.
- Clean out the medicine chest regularly.
- Dispose of old medications.
- Store all medicines, sprays, powders, cosmetics, mouthwashes, etc., out of reach in locked cabinets.
- Keep all cleaners, household products and medications in original safety top containers.
- Store all bleaches, soap and detergent out of reach.
- Store household cleaning products in locked cabinets.
- Store insect spray and weed killers in locked area.
- Keep gasoline and car products in locked area. Store turpentine, paints and paint products in locked area
- Most poisonings from household products, to children and adults, occur when the product is in use, not when it is stored.
- Children under 5 are the most likely to eat, drink, inhale or splash themselves with toxic products.
- Over-the-counter medications are involved in more poison emergencies than prescription medications.

